Case Study
This page is based on:
Jones, Geoffrey (2014). Magnetic prospection for datable materials. Presented at the 2014 Plains Anthropological Society Conference, Fayetteville AR, October 28-November 1, 2014.
Thermal features, such as hearths and burned structures, are often detectable in magnetic surveys. These features are rich sources of archaeological data. In particular, thermal features are sought as sources of datable material. Among the dating methods that require or can be performed on burned or thermally-altered materials are:
- Radiocarbon
- Archaeomagnetism
- Paleointensity
- Thermoluminescence
- Dendrochronology
- Potassium-argon
Magnetic surveys can map many features across a site, and these can be targeted specifically for datable materials. This allows more samples to be collected efficiently and with minimal disturbance.
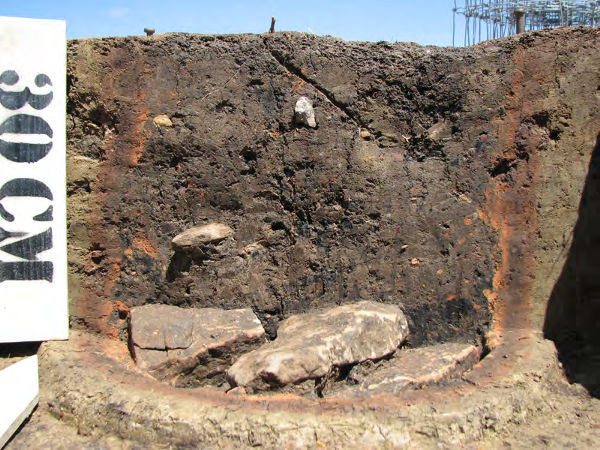


The fill of the hearth contains charcoal that could be (and was) dated more accurately and cheaply than could be done with these other methods, but this carries with it an opportunity. Archaeomagnetism and paleointensity are only useful if samples can be compared to regionally specific curves tracking the history of the geomagnetic field. These curves can only be built by correlating data from magnetic samples against independent techniques such as radiocarbon and dendrochronology. Such curves do not yet exist for the region where this hearth occurs, but would be very useful for dating features that lack charcoal. Paleointensity also offers the potential to date unoriented magnetic samples, including ceramics.
Radiocarbon dating may generally be considered the most useful and cost-effective physical dating method for archaeological investigation. The preservation advantage of charcoal over unburned wood makes it a common source of datable carbon. The hearth, as a locus of food preparation may also offer other datable materials such as bone or maize cobs. The magnetic enhancement of burned features makes it possible to map and target them as sources of datable carbon.
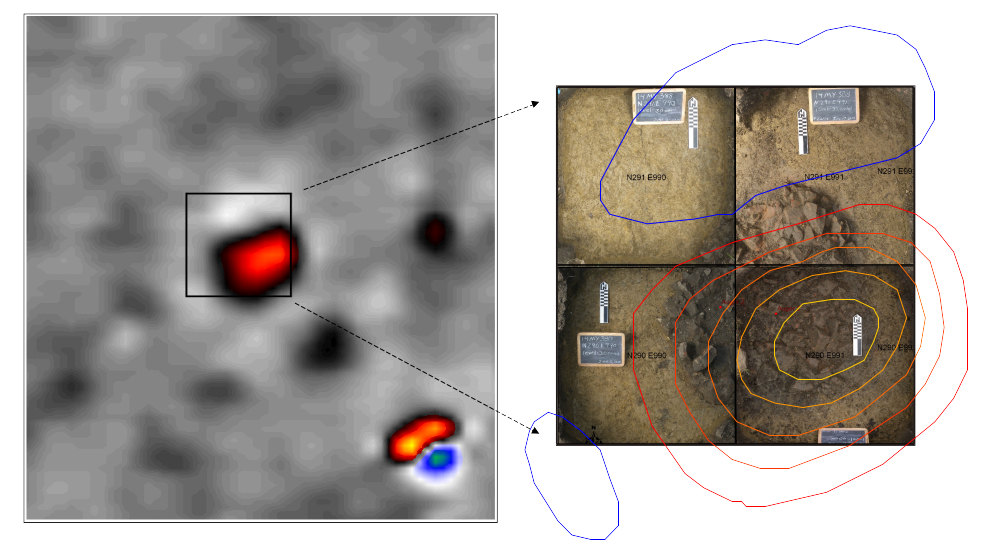
The Eagle Tree site (48CO2920) in northeastern Wyoming offers an example of the use of magnetic survey for targeting datable features. Eagle Tree was a spatially extensive prehistoric campsite with a very sparse distribution of features and artifacts. It was the subject of archaeological mitigation performed by GCM Services, Inc. prior to mining. Magnetic survey identified a number of subsurface features, and allowed efficient recovery of far more data than might have been possible with conventional archaeological techniques alone.
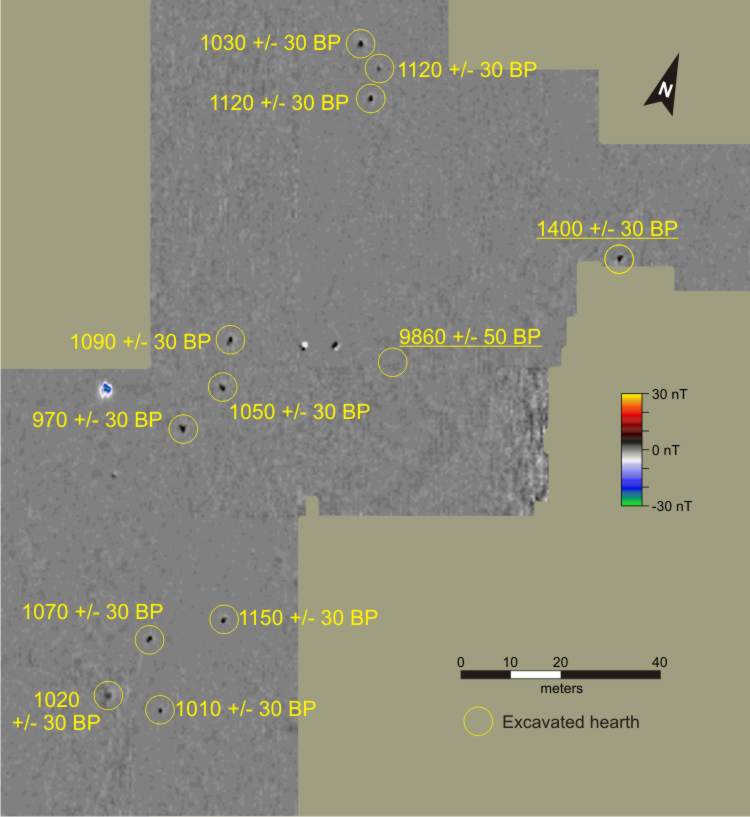
Mitigation at Eagle Tree also involved the search for older components in the deeply stratified sediments. The magnetometer is limited to approximately one meter in its range of detection of prehistoric features. At Eagle tree it was used in conjunction with mechanical excavation to investigate at greater depths. Successive iterations of mechanical stripping and magnetic survey of the stripped surface were performed. The aim of this approach was to open a large area for investigation, while being able to detect features before they were impacted. Features and associated occupation surfaces could then be excavated by hand (this approach has been successful elsewhere).

Dendrochronology relies on having a known local history of tree growth patterns. Although it does not require that a sample be burned, in many environments, samples are unlikely to survive without the preservation advantage of charcoal over unburned wood. The magnetic effects of burning can also offer a means for locating samples through magnetic survey, through locating features such as burned houses of palisades. Of course, burned timbers are likely to be datable by radiometric means, but if a local dendrochronology has been established, it is a more precise dating method (with the understanding that both date the death of the tree, rather than the use or burning of the wood). Conversely, radiocarbon dates may be of value in anchoring dendrochronologies. Dendrochronology has also been important in establishing archaeomagnetic curves and calibrating radiocarbon dates. Aside from its value for dating, tree-ring data may be of interest for its implicit climate information.
The Eastview site is an example of burned timbers found in a structure identified with magnetic survey. The house at Eastview was excavated as part of a field school conducted by Courson Archaeological Research. Although dendrochronology was not performed at the site, it illustrates how datable timber samples might be directly targeted.
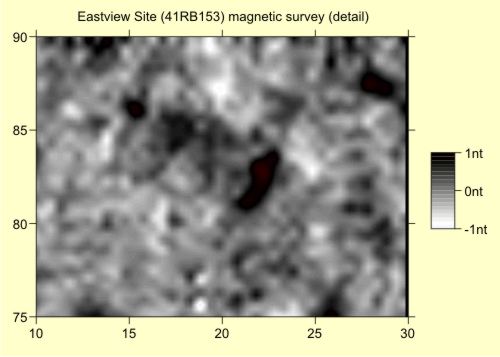
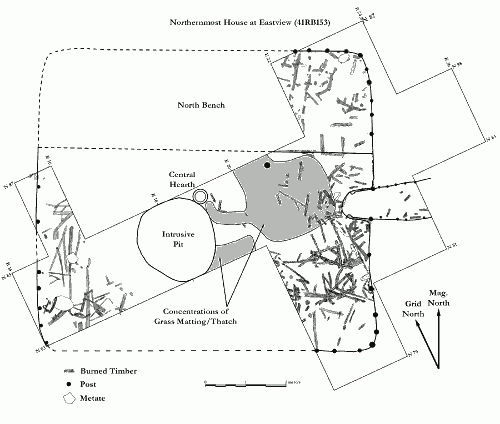

The hearth has played a central role on many human activities. It is often a focus of food processing, shelter, crafts, and social life. Burned structures can offer superior preservation and a snapshot of daily life.
The spatial dimension inherent in magnetic survey results can contextualize temporal data, especially on multicomponent sites. Beyond a narrow focus on dating, geophysical survey (magnetic and otherwise) can be used to search materials for useful for a wide variety of analyses, including botanical, faunal, lipids, soil chemistry, etc…
While magnetometry is not effective on every site, where it can be applied it has the potential to broaden the range of temporal questions that may be asked, and to help answer them cost-effectively and in greater detail.
References:
1. Tomasic, John (2013). 2012 Phase IV Excavations of 14my388 at the Eastep Riverbank Stabilization Project, an Nrcs Undertaking In Montgomery County, Kansas. With contributions by: Rolfe D. Mandel; Edwin J. Miller; Andrew Wyatt; Rebecca Freidel; Whitney Cleaver. Kansas State Historical Society.
See also: Case study: The Eastep Site; The Eastep Site Revealed (Kansas Preservation, Fall 2010) by John Tomasic.
2. Munson, Gene (2014). Fieldwork Completion Report for Eagle Tree Site (48CO2920). Prepared for Antelope Coal, LLC, Gillette, Wyoming. GCM Services, Inc. Butte MT.
Jones, Geoffrey (2013). Magnetic survey at Eagle Tree Site (48CO2920). Archaeo-Physics LLC Report of investigation No. 199. Prepared for GCM Services, Inc. (Butte Montana). Archaeo-Physics, LLC. Minneapolis, MN.
3. Munson, Gene (2013). Excavation Of Holmes Draw Site (48CA2834): A Paleoindian, Early Plains Archaic, Middle Plains Archaic And Late Prehistoric Campsite. With Contributions by: Geoffrey Jones; John Albanese; David McKee; Viktor Kujawa; PaleoResearch Institute; Beta Analytic, Inc. Prepared for Peabody Powder River Operations, LLC, Gillette, Wyoming by GCM Services, Inc., Butte, Montana.
4. Case study: The Eastview Site; Insights from the Eastview Site, The Newsletter of the Panhandle Archaeological Society, Oct. 2013, by Scott D. Brosowske.
